Printed and organic electronics » Innovative everyday heroes
Flexible, organic and printed electronics: Limitless Innovation
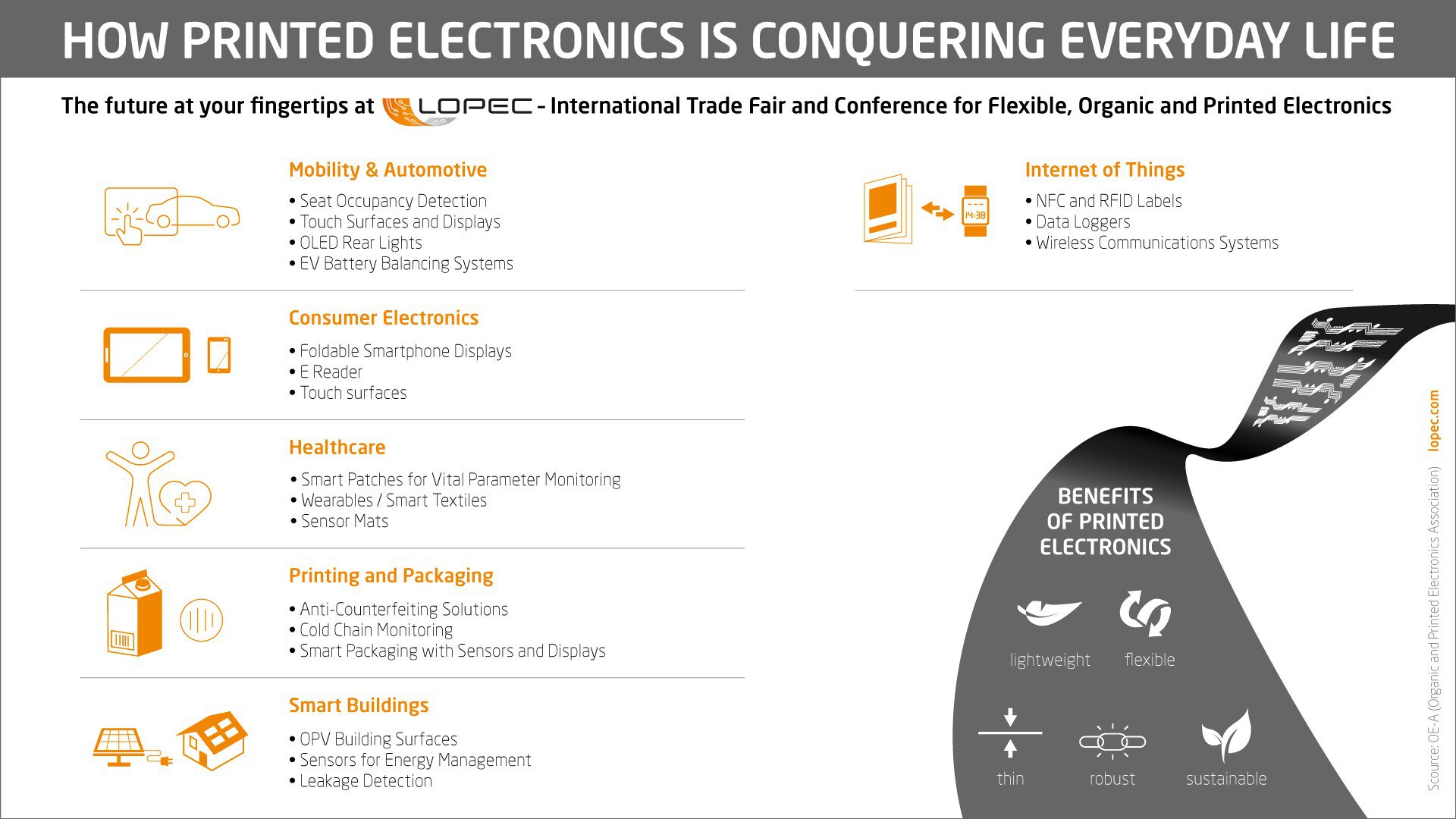
Flexible, organic and printed electronics are conductive polymers and inks that can be printed onto foil, paper, glass, or fabrics, across large areas and at low cost. Compared to conventional electronics, these electronic components offer a number of benefits: They are extremely thin, flexible and lightweight . They can be used for a wide range of applications, e.g., in consumer electronics, packaging, the automotive industry, pharmaceuticals, energy, or white goods.
The results include flexible displays, test strips, integrated seat sensors, printed antennas, smart labels, and flexible, printed sensors for a variety of applications.
A number of terms are used to describe flexible, organic and printed electronics, including:
- Flexible Electronics
- Flexible, hybrid electronics
- Green electronics
- Organic Electronics
- Conductive synthetics/polymer electronics
- 3D structural electronics
- Large-area electronics
- Thin-film electronics
- Plastic electronics
- Abbreviations such as OLAE or FOLAE (flexible organic and large-area electronics)
All of these terms essentially refer to the same thing: Electronics applied in a way that goes beyond the traditional approach.
Flexible and organic electronics are used in printed sensors, solar cells, keyboards, and displays, car interior thereby turning simple products into smart objects, luminous wallpapers in advertisement or food packaging that allows continuous tracking of the cold chain, open up new possibilities for the industries. Organic photovoltaic cells (OPV) that can cover entire building facades offer a fresh impetus for the energy sector.
Printed Electronics enables sustainable products
PE Printing processes are very energy efficient compared to conventional production processes. As an additive process, printing consumes less material and reduces the amount of waste needing disposal or treatment. The materials used are often organic chemicals and non-hazourdous to the environment, hence recycling is possible. On the product side, the use of printed electronics pays off, too. It saves material and reduces the weight of a product.
For example: In electric cars, printed sensors and flexible electronic components can replace traditional cable harnesses and rigid parts. This reduces the vehicle's weight, which lowers energy consumption and increases the battery's range.
Another example: In wearables, such as fitness wristbands or medical patches, printed electronics enable ultra-light, flexible designs with integrated functions, such as temperature or motion sensors. These designs use less material and offer high energy efficiency.
At LOPEC the flexible, organic and printed electronics industry presents its technology and applications which enable more sustainable products for Smart Living, Mobility and other markets. Visit LOPEC and see e.g. how PE can help to prevent food waste, lessens fuel consumption or generates cleanest electricity.
Sustainability advantages of Flexible, Organic and Printed Electronics:
Design/Products
- Weight & space reduction
- Less material usage
Process/Production
- Power efficiency
- Additive production
- Free of chemicals
- Renewable polymers